Laser technology was pioneered in the mid-twentieth century and has come a long way
since the first prototype. Today, lasers are one of the most popular tools in the manufacturing
industry. And for good reason lasers have allowed us to effortlessly perform complex
processes with ultrafine outcomes.
What is Laser Cutting Technology?
Laser cutting is a technology that uses a focused laser beam to cut materials, such
as metal, plastic, wood, or glass. The laser beam is generated by a high-power laser and is
precisely focused onto the material using a lens or a mirror. As the laser beam moves across
the material, it melts, burns, or vaporizes it, leaving a clean, precise cut edge.
The Advantages of Laser Technology

a). More Accurate
The advanced laser beams of today can be focused down to a thousandth of a millimetre.
This means that any measuring, marking, or cutting can be done with absolute precision.
With computer chips and medical device components getting increasingly minuscule, laser
technology offers superior accuracy and consistency that cannot be achieved with traditional
machining equipment.
Laser cuts are also incredibly clean, leaving no distortion or burrs on the remaining material.
This negates the need for an additional step to clean or finish the product after laser
processing.
b). Easy to Automate
With Industry 4.0 focusing on automation and the integration of technology with
manufacturing, laser technology can easily be added to production lines to achieve
unprecedented standardization.
Using lasers in manufacturing can lead to shorter cycle times, less maintenance, and more
cost-effective production. Previously labour-intensive and error-prone operations can be
done simply and flawlessly. When laser technology is combined with automation, processes
can be completed at astonishing speeds. Lasers are currently the quickest method of cutting
and welding on the production line.
c). Flexible Uses
Lasers can work on a diverse range of materials including fabric, plastic, glass, and metal.
Because laser parameters can be adjusted at any time, a single laser can perform numerous
manufacturing tasks such as cleaning, etching, cutting, or welding.
Unlike other comparable technologies, most laser machines are contactless, allowing them
to be used on objects of various geometrical complexities while maintaining the integrity of
their surfaces.
Investing in laser equipment has a high return on investment as it reduces redundancies
and streamlines operations. The applications of lasers are increasing each day, providing
more potential for the manufacturing floor.
d). Better for the Environment
Lasers use a fraction of the energy of their conventional counterparts. More efficient energy
consumption is essential for companies that want to lower production costs and reduce their
emissions and carbon output.
Lasers can also replace manufacturing methods that require consumables like welding
fluxes, steel grits, or ink and labels. This prevents a considerable amount of waste and
avoids the emissions associated with having to produce and transport these consumables
as well.
Finally, laser equipment can be remarkably compact, allowing manufacturers to build more
economical production lines and work within a smaller, more optimized factory footprint.
Top Applications of Lasers
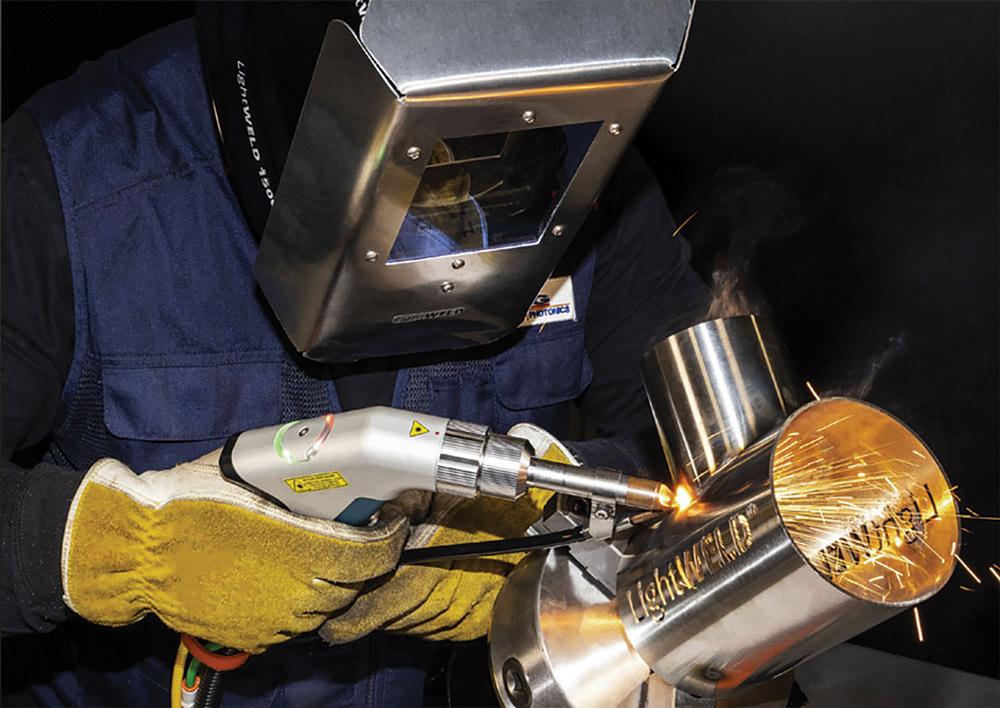

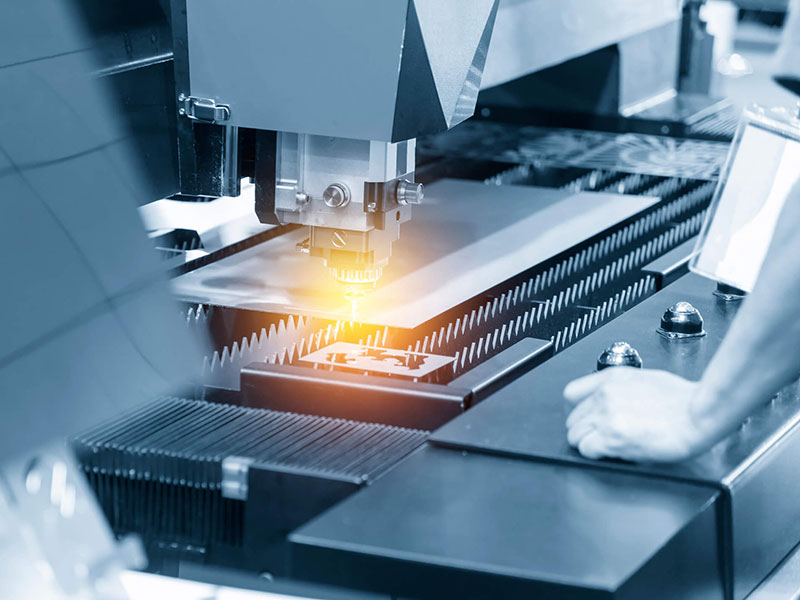


a). Laser Cutting
Laser cutting uses a focused high-power laser beam to rapidly irradiate material and
produce very fine cuts or patterns. Lasers can effortlessly slice through dense materials
such as titanium or steel with smooth incisions and no mechanical or heat stress in the
surrounding areas.
Laser cutting technology is superior to conventional cutting machines because its operations
can be performed at ultrafast speeds, with micron-level precision and repeatable
consistency. Since the material stays stationary during the whole process it does not sustain
any surface wear.
b). Laser Engraving
Laser engraving uses the same laser beam to make a material’s surface vaporize instantly
as it marks out a barcode, character, or pattern. Laser engraving is now one of the most
popular marking methods due to its fast production speed and quick repetition cycles
UV laser engraving is extremely powerful and is commonly used to imprint permanent
unique identification numbers on components and products to ensure manufacture
traceability. UV laser engraving is highly durable and can be applied on surfaces that are
flat or curved.
c). Laser Welding
Laser welding is very effective for complex materials that cannot be handled by conventional
methods. It works by using laser radiation to melt material down to a molten and joinable
state. No electrodes are needed and therefore no contamination or deformation to the
material occurs.
A large range of materials can be welded together by laser, including two different kinds of
metals or a metal and a plastic. Although laser welding is precise enough to form welds
smaller than a millimetre, these welds are much stronger than they would be if using
traditional soldering or glue.
d). Laser Texturing
Laser texturing uses controlled laser ablation to remove specific materials from the surface
of an object. This process is generally used to create additional roughness and textural
micro-patterns such as dimples and freeform grooves on a material’s surface.
Creating surface textures can improve the performance of certain components. For
example, rough textures on medical implants can provide additional surface area for new
tissue to anchor. Likewise, laser textured mechanical seals have improved lubricant
retention and durability.
Conclusion:
Laser technology is quickly replacing many tedious mechanical processes. Automated laser
machines create safer manufacturing floors by eliminating risky manual processes. Through
investing in laser technology, manufacturers can improve productivity, lower operation
costs, reduce maintenance, and produce exceptionally accurate and repeatable results.





